- 形成层

形成层
概述
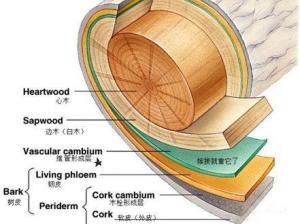 形成层裸子植物和 双子叶植物的根、茎中 木质部和 韧皮部之间的一种 分生组织.分两种:(1) 维管形成层,它有 分生活动,可不断产生新的木质部和韧皮部,使 根茎不断加粗.(2) 木栓形成层,向外产生木栓层、向内产生 栓内层.形成层 细胞有两种类型:(1) 纺锤状原始细胞, 细胞核多为椭圆形或肾形,两端尖锐扁长形, 液泡大而明显或小而分散,胞质稀薄,细胞 径向壁较厚,其上具单 纹孔.(2) 射线原始细胞,近等径,具 薄壁组织细胞的特征.形成层 薄壁细胞的活动,受外部环境、尤其是温度和水分的影响.温带树木的形成层, 从春天开始活动,主要进行 平周分裂,分别构成 次生木质部和 次生韧皮部.冬天形成层原始细胞处于休眠状态,如此年复一年,在茎的 横断面上,就形成了 年轮.形成层细胞的活动一般可持续数月,但常随地球纬度高低而变化.Gymnosperms and dicotyledonous plant roots, stems between the xylem and phloem of a meristem. In two ways: (1), vascular cambium, it had a hand hygiene activities to continuously produce new xylem and phloem, roots continued to make bold. (2) cork cambium, cork layers produced outward, inward and produce phelloderm. cambium cells, there are two types: (1) the original spindle-shaped cells, nuclei are mostly oval or kidney-shaped, sharp at both ends of prolate shape, vacuoles, large and obvious, or small and scattered, thin cytoplasm, cell radial wall thick, on which a single pit. (2) Ray primitive cells, near-Drive, a thin wall tissue characteristics. parenchyma cells form a layer of the activities by the external environment, especially temperature and moisture effects. temperate trees, cambium, from spring to begin its activities, mainly carried out periclinal divisions, respectively, constitute the secondary xylem and secondary phloem. form a layer of primitive cells in the winter of hibernation, so year after year, in the stem cross-section on the rings formed. cambium cell activity typically lasts several months, but often varies with the high and low latitude on the earth .
形成层裸子植物和 双子叶植物的根、茎中 木质部和 韧皮部之间的一种 分生组织.分两种:(1) 维管形成层,它有 分生活动,可不断产生新的木质部和韧皮部,使 根茎不断加粗.(2) 木栓形成层,向外产生木栓层、向内产生 栓内层.形成层 细胞有两种类型:(1) 纺锤状原始细胞, 细胞核多为椭圆形或肾形,两端尖锐扁长形, 液泡大而明显或小而分散,胞质稀薄,细胞 径向壁较厚,其上具单 纹孔.(2) 射线原始细胞,近等径,具 薄壁组织细胞的特征.形成层 薄壁细胞的活动,受外部环境、尤其是温度和水分的影响.温带树木的形成层, 从春天开始活动,主要进行 平周分裂,分别构成 次生木质部和 次生韧皮部.冬天形成层原始细胞处于休眠状态,如此年复一年,在茎的 横断面上,就形成了 年轮.形成层细胞的活动一般可持续数月,但常随地球纬度高低而变化.Gymnosperms and dicotyledonous plant roots, stems between the xylem and phloem of a meristem. In two ways: (1), vascular cambium, it had a hand hygiene activities to continuously produce new xylem and phloem, roots continued to make bold. (2) cork cambium, cork layers produced outward, inward and produce phelloderm. cambium cells, there are two types: (1) the original spindle-shaped cells, nuclei are mostly oval or kidney-shaped, sharp at both ends of prolate shape, vacuoles, large and obvious, or small and scattered, thin cytoplasm, cell radial wall thick, on which a single pit. (2) Ray primitive cells, near-Drive, a thin wall tissue characteristics. parenchyma cells form a layer of the activities by the external environment, especially temperature and moisture effects. temperate trees, cambium, from spring to begin its activities, mainly carried out periclinal divisions, respectively, constitute the secondary xylem and secondary phloem. form a layer of primitive cells in the winter of hibernation, so year after year, in the stem cross-section on the rings formed. cambium cell activity typically lasts several months, but often varies with the high and low latitude on the earth .


 求购
求购

